FAQs
-
Introduce energy labels
I. Confirmative energy label
1. Understanding the Label: Confirmative energy label is the label showing the energy saving symbol (also known as Viet Energy Star) affixed to means, equipment circulating in the market as these means and equipment have the level of energy efficiency meeting or exceeding the high energy performance (HEP) prescribed by the Ministry of Industry and Trade for each period.
2. The color and size of confirmative energy label are specified as follows:

II. Comparative energy label
1. Understanding the label: the label affixed to means and equipment circulating in the market which have different energy performance levels corresponding with five levels of energy performance (one star to five stars; five-star label shows the best energy performance) to provide consumers with information on the energy performance of one mean or equipment compared to other means or equipment of the same type in the market, helping consumers choose means and equipment with lower energy consumption.
The images of comparative energy labels shown below correspond to five levels of energy performance as prescribed (by the number of stars on the label):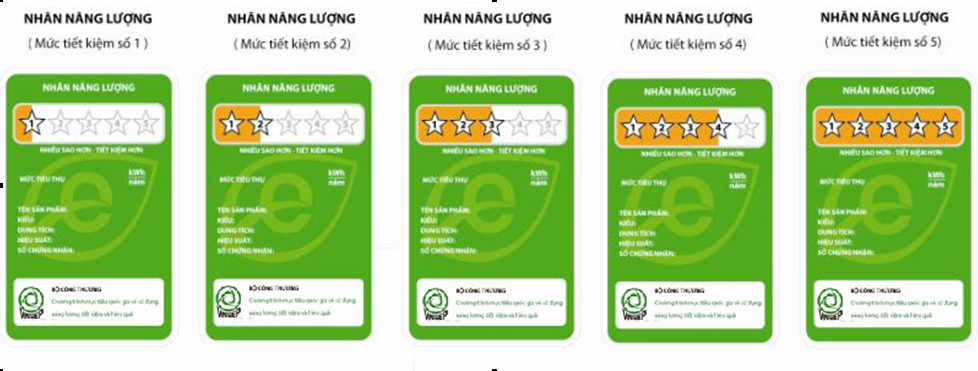
2. The color and size of comparative energy label are specified as follows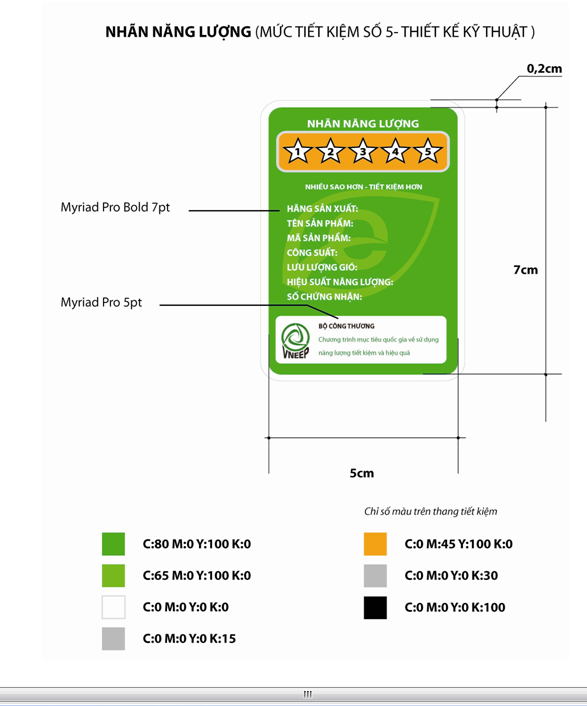
3. Information which must be shown on the label
Comparative energy label must contain at least the following information:
a) Certification Code: A code issued by the Ministry of Industry and Trade to serve the management, specified in the Certificate of energy saving product.
b) Name/code of product: The code or name of the product registered by the business and issued by the Ministry of Industry and Trade in the Certificate of energy saving product
c) Manufacturer: The name of the organization / enterprise producing the product and registering for energy labeling
d) Importer: The name of the organization / enterprise importing the energy labeled product (this information only applies to importers)
e) The part showing energy efficiency parameters (energy performance level): The amount of energy consumed in one operation hour of products of the same category but produced by different manufacturers is divided into 5 levels corresponding with the number of stars on the label (from one star to five stars). The energy efficiency level (energy performance level) is determined by the Ministry of Industry and Trade through evaluating the testing results of energy efficiency of the product shown in the Certificate of energy saving product.
f) Energy consumption level of the product: the energy consumption level is calculated in kWh per year.
g) Other Information: defined in detail in the Decision on granting the certificate appropriate for each specific product.
MOIT -
What is Cleaner Production?UNEP defines cleaner production as
....the continuous application of an integrated preventive environmental strategy applied to processes, products, and services in order to increase efficiency and reduce risks to humans and the environment.
For production processes: Cleaner production includes conserving raw materials and energy, eliminating toxic raw materials, and reducing the quantity and toxicity of all emissions and wastes- For products: Cleaner production includes the reduction of negative impacts along the life cycle of a product, from raw material extraction to its ultimate disposal; and
- For services: Cleaner production is to incorporate environmental concerns into designing and delivering services.
Cleaner production is different from end-of-pipe treatment, i.e. treatment of air emissions, wastewater and solid waste. With end-of-pipe treatment you reduce the pollution load, but you do not recover the lost raw materials. Therefore, end-of-pipe treatment is always expenditure, whereas cleaner production brings economic benefit in addition to the reduced pollution load. Cleaner production is the same as waste minimisation and pollution prevention. Cleaner production is also a useful step towards environmental management, e.g. ISO 14001
-
Benefits of Cleaner Production
Cleaner production is relevant to all industries, whether they are small or big, or they have a low or high consumption of raw materials, energy, and water. For far the most companies, there is a potential of reducing the resource consumption with 10-15%!
Cleaner enterprises are better enterprises
Why? Because cleaner enterprises have minimised their losses of raw materials and products, thus giving them a higher production yield and an overall better economy and competitiveness.Benefits of Cleaner Production
- Improved production efficiency;
- Better utilisation of raw materials, water and energy;
- Recovery of valuable by-products;
- Less pollution;
- Lower cost for waste disposal and wastewater treatment;
- Improved public image; and
- Improved occupational health and safety.
Less use of raw materials and energy
The most convincing benefit of cleaner production is its ability to reduce the consumption of resource and materials.Savings in energy and materials bring direct reductions in production costs, which again make the company more competitive.With the increasing cost of raw materials, energy and water, no company can afford to lose these resources in the form of waste.New and improved market opportunities
Increasing consumer awareness of environmental issues has led to a spurt in demand of green products in the international market. Consequently, if you put in conscious efforts towards cleaner production, you open up new market opportunities and produce better quality products, saleable at a higher price.
Better access to finances
Investment proposals based on cleaner production contain detailed information on the economic, technical and environmental feasibility of the planned investment. This gives a very solid basis for achieving financial support from banks or environmental funds.
On the international market, financial institutions are awakening to the problems of environmental degradation, and are now scrutinising applications for loans from an environmental angle.
Better image of your company
Cleaner production reflects and improves the overall image of your company. Needless to mention, a company with a green image has a better acceptance both by the society as well as the regulatory authorities.
ISO 14000
Cleaner production will make it much easier to implement an environmental management system such as ISO 14000. This is because most of the initial work already has been carried out through the cleaner production assessment. An ISO 14000 certificate can be a market opener, giving better access to export markets. Having made a cleaner production assessment will maker it much easier to implement an environmental management system as ISO 14001.
Better working environment
Apart from improving the economical and environmental performance, cleaner production can also improve the occupational health and safety conditions for the employees.
Favourable working conditions can boost the morale of staff and at the same time foster a concern for controlling waste. Such actions will help your company gain a competitive edge.
Better compliance with environmental regulations
Meeting the regulatory standards for discharge of wastes (liquid, solid or gaseous) requires often installation of expensive and complex pollution control systems like wastewater treatment plants.
With cleaner production the treatment of residual effluents normally becomes easier and cheaper. This is because cleaner production leads to an all round reduction in wastes: volume-wise; load-wise; and even toxicity-wise! -
Examples of Cleaner Production Options
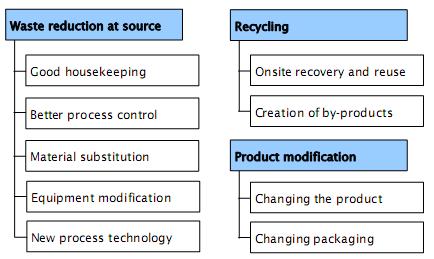 Cleaner Production Options relates not only to changing equipment, but also to the operation and management of the company. Cleaner Production Options can be grouped into:
Cleaner Production Options relates not only to changing equipment, but also to the operation and management of the company. Cleaner Production Options can be grouped into:
- Waste reduction at source;
- Recycling; and
- Product modifications.
Waste reduction at source
Going to the source of pollution is the fundamental idea of cleaner production.
Good housekeeping is the simplest type of the cleaner production options. Good housekeeping requires no investments and can be implemented as soon as the options are identified. Good housekeeping is e.g. to repair all leaks and avoid losses by closing water taps and turning off equipment when not needed. Even though good housekeeping is simple, it requires focus from the management and training of staff.
Better process control is to ensure that the process conditions are optimal with respect to resource consumption, production and waste generation. Process parameters such as temperature, time, pressure, pH, processing speed, etc. have to be monitored and maintained as close to the optimum as possible. As with good house keeping, better process control requires improved monitoring and management focus.
Material substitution is to purchase higher quality materials that give a higher efficiency. Often there is a direct relation between the quality of the raw materials and the amount and quality of the products. Material substitution is furthermore to replace existing materials with some that are environmentally better.
Equipment modification is to improve the existing equipment so less material is wasted. Equipment modification can be to adjust the speed of an engine, to optimise the size of a storage tank, to insulate hot and cold surfaces, or to improve the design of a crucial part of the equipment. One example from electroplating is to construct drip hangers to recover drag out from the plated parts.
New process technology is to install modern and more efficient equipment, e.g. a highly efficient boiler or a jet-dyeing machine with a low liquor ratio. New process technology requires higher investments than the other cleaner production options and should therefore be considered carefully. However, the potential savings and quality improvements often pays back the investment in a very short time.
Recycling
Waste streams that are unavoidable might be recycled within the company or might be sold as by-products.
On-site recovery and reuse is to collect "waste" and reuse it in the same or a different part of the production. One simple example is to reuse rinse water from one process to another cleaning process.
Creation of by-products is to collect (and treat) "waste-streams" so they can be sold to consumers or to other companies. Excess yeast from a brewery can for instance be used for pig fodder, fish farming or as a food additive.
Product modification
Improving the products so they pollute less is also a fundamental idea of cleaner production.
Changing the product is to re-think the product and the requirements to the product. For instance, if it is possible to replace a painted metal shield with a plastic shield for a certain product, then the environmental problems and costs related to paint finishing could be avoided. Improved product design can result in large savings on material consumption and use of hazardous chemicals.
Changing packaging can be just as important. The key word is to minimise the packaging and maintaining the protection of the product. One example is to use recycled cardboard instead of plastic foam for protection of fragile items.



